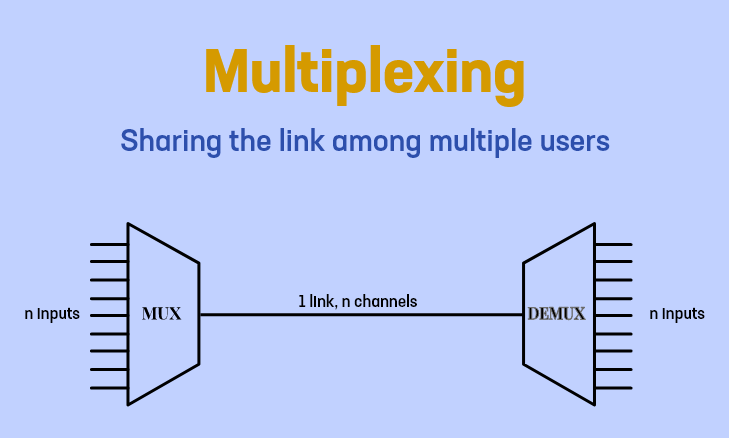
Multiplexing and switching
- Multiplexing is a technique used for transmitting signals simultaneously over a single communication link
- Multiplexing is done to utilize the available bandwidth properly and to improve the efficiency during a transmission.
- Each part of the communication link being used for carrying transmission between an individual pair of input and an output line is referred to as a channel.
Why we need Multiplexing in a communication channel?
There are the following reason that why multiplexing is needed in a communication:-
- To send several signals simultaneously over a single communication channel.
- To reduce the cost of transmission.
- To effectively utilize the available bandwidth of the communication channel.
Techniques of Multiplexing
It can be done using three techniques:-
- Frequency divisional multiplexing: FDM is used when the bandwidth of the transmission medium is greater than the total bandwidth require-ment of the signals to be transmitted. It is often used baseband analog signals.
-
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing:
WDM is an analog multiplexing technique designed to make use of the high data rate capability of fibre-optic cables.
A fibre-optic cables has a much higher data rate than coaxial and twisted pair cables and using it as a single link wastes a lot of precious bandwidth.
In WDM, the multiplexing and demultiplexing are done with the help of a prism, which bends the light beam by different amount depending on their angle of incidence and wavelength.
-
Time-Divison Multiplexing:
TDM is a digital multiplexing technique that allows the high bandwidth of a link to be shared amongst several signals.
Unlike FDM and WDM, in which signals run at the same time but with different frequencies, in TDM, signals operate at the same frequency but at different times. In other words, the link is time-shared instead of sharing parts of bandwidth among various signals.


What is MEANT BY TERM Switching?
On a network, switching means vanquish traffic by setting up temporary connections between two or more network points.
This is done by devices located at different locations on the network, called switches(or exchanges).
Switches create short-term connections amongst two or more devices connected to them. In a switched network, some switches are straight connected to the communicating devices, while others are used for routing or forwarding information.
Switching Technique
-
Circuit Switching:
When a device wants to transfuse with another device, circuit switching technique creates a fixed-bandwidth channel, called a circuit, between the source and the destination. This circuit is a physical path that is reserved exclusively for a particular details flow, and no other flow can use it.
-
Packet Switching:
Packet switching introduces the concept of seperate data into packets, which are discrete units of potentially variable length blocks of data. Apart from data, these packets also contain a header with control information such as the destination address and the priority of the message.

-
Message switching:
A message switching is a unit of information which can be varying length. Message switching is one of the unseasonable types of switching techniques, which was common in the 1960s and 1970s. This switching technique employs two mechanisms
1. STORE AND FORWARD MECHANISM
2. BROADCAST MECHANISM












